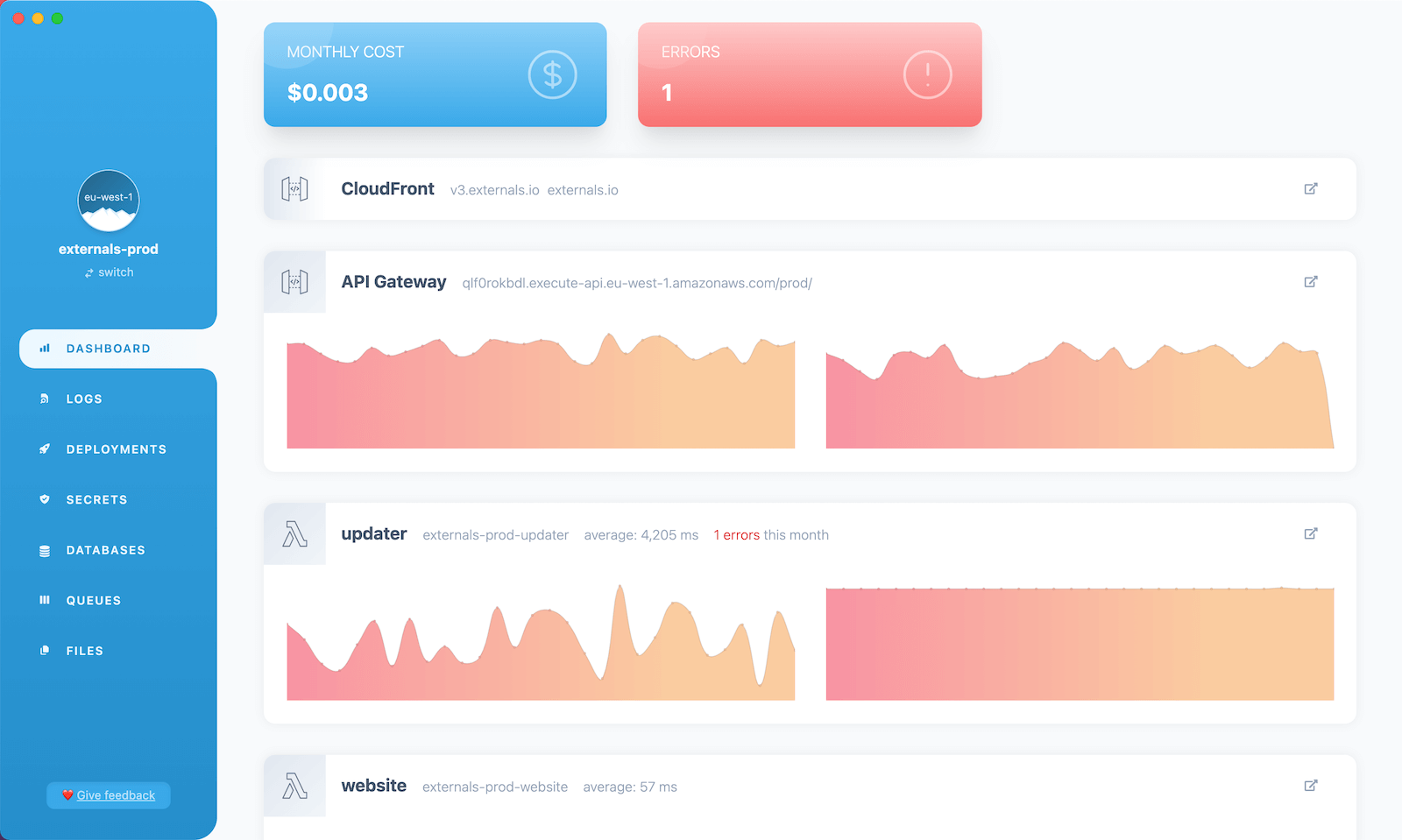
Monitoring
By default, AWS Lambda publishes PHP logs and metrics to AWS CloudWatch (opens in a new tab). These include HTTP response times, code execution duration, error rates, and more.
Here is a summary of recommended tools for monitoring Bref applications:
- Logs and metrics: CloudWatch (built-in), Bref Cloud
- Error tracking: Sentry (opens in a new tab) and similar services
- Performance tracing: Bref Cloud with X-Ray
Let's dive into the details of each of them.
Sentry
Sentry (opens in a new tab) is a popular error tracking service. It works well out of the box with Bref for HTTP applications: install the Sentry SDK for PHP (opens in a new tab) (or the Laravel (opens in a new tab) or Symfony (opens in a new tab) integrations) and errors will be tracked automatically.
For more advanced use cases, such as tracking Lambda errors outside of PHP-FPM (timeouts, oversized responses…), monitoring event-driven handlers (SQS, EventBridge, S3…), or tracking cold starts and AWS SDK calls, the Bref Sentry package extends Sentry's capabilities for AWS Lambda. It is available as a separate license.
Bref Cloud
Bref Cloud provides an all-in-one monitoring experience for serverless PHP applications:

- Logs: view and search CloudWatch logs in a simplified UI.

- Metrics: monitor Lambda invocations, duration, errors, and more.
- Traces: visualize X-Ray traces to understand the performance of your application, including database queries, HTTP calls, and AWS SDK calls.

With the Bref X-Ray package, traces are enriched with annotations that you can use to filter and search. For example, you can filter traces by specific controller, route, CLI command, or job class:
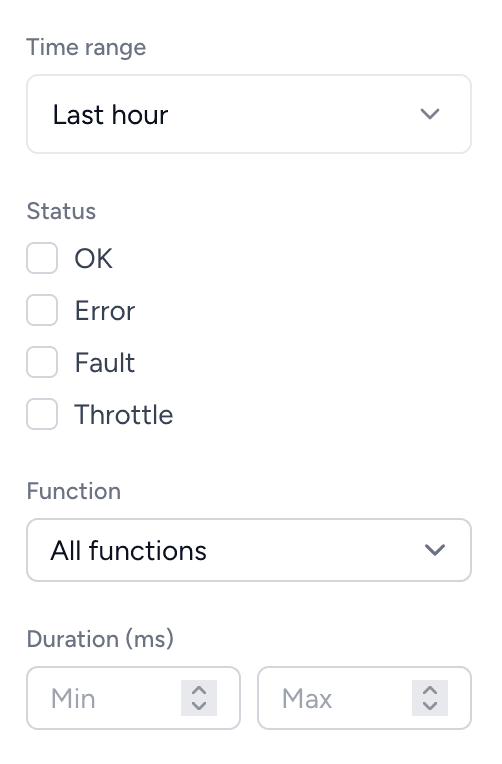
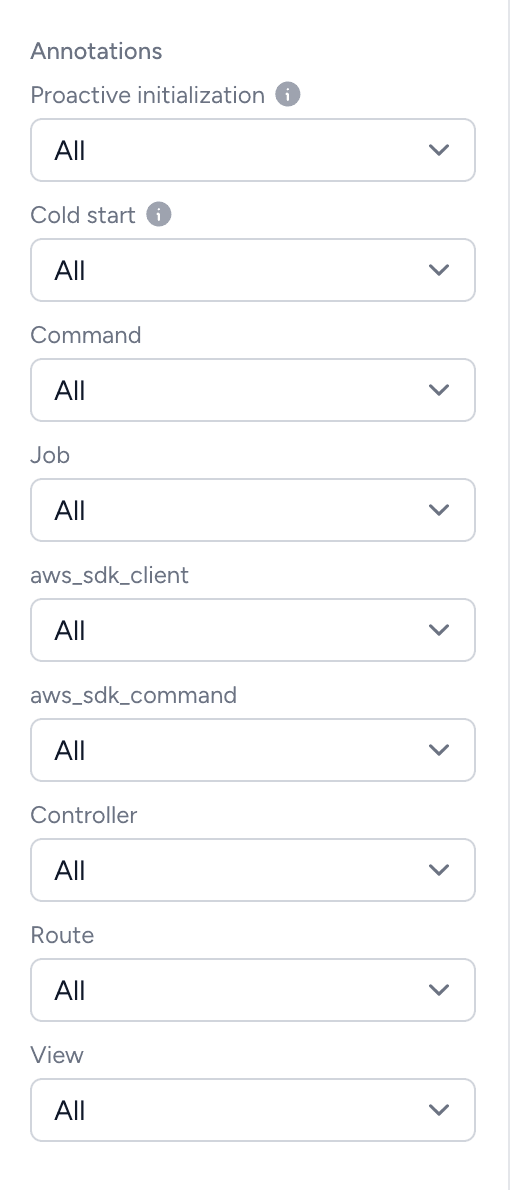
Bref Cloud users get a free Bref X-Ray license included in their plan to enable performance tracing. To activate it, contact support via bref.cloud/support (opens in a new tab) or Slack (opens in a new tab).
X-Ray
AWS X-Ray (opens in a new tab) provides distributed tracing for Lambda applications. The Bref X-Ray package integrates X-Ray with PHP, tracking cold starts, database queries, HTTP calls, AWS SDK calls, and more. It supports both Laravel and Symfony.
The package can be used with or without Bref Cloud. Bref Cloud users get a free license (see above), while others can purchase a standalone license.
Sentry Lambda package
As mentioned above, the standard Sentry SDK works great for HTTP applications. The Bref Sentry package goes further by adding Lambda-specific capabilities: tracking errors outside of PHP-FPM, monitoring event-driven handlers, and tracking cold starts.
The package can be used with or without Bref Cloud. It is available as a standalone license.
Bref Dashboard
The Bref Dashboard (opens in a new tab) is an alternative for projects that do not use Bref Cloud. It fetches data from AWS CloudWatch and provides a simple UI for logs and metrics. It requires no setup in AWS and can be used straight away.
Tideways
Tideways (opens in a new tab) is a PHP-specific monitoring and profiling tool that can be used with Bref. It requires setting up a daemon on an EC2 instance in a VPC.